
Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life when she stops having periods and her reproductive hormones change. It usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, but it can vary for each woman.
While menopause brings about many changes in the body, one of the common concerns that women face is hair loss. Understanding the causes of menopausal hair loss and how to manage it can help ease worries and maintain healthy hair. Let’s explore this topic further.
What is Menopausal Hair Loss?
Menopausal hair loss refers to the excessive shedding or thinning of hair that some women experience during menopause. Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s life when her menstrual cycles stop and her hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone, decrease.
These hormonal changes can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to hair loss. In addition, during menopause, the hair follicles may become more sensitive to androgens (male hormones), such as testosterone, which can further contribute to hair thinning and hair fall.
As a result, women may notice a decrease in hair volume, increased hair shedding, or the appearance of thinning areas on the scalp. Menopausal hair loss can vary in severity and pattern. Some women may experience mild hair thinning, while others may notice more noticeable hair loss in specific areas.
Not all women will experience significant hair loss during menopause, and genetic factors and overall health can influence the extent of hair loss. While menopausal hair loss can be distressing, understanding its causes and available treatment options can help women manage and cope with these changes.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or dermatologist can provide further guidance and personalized advice for addressing menopausal hair loss.
Causes of Menopausal Hair Loss
Hair loss during menopause can happen because of a few reasons. However, the main causes are related to hormone changes and aging. Here are the main things that can lead to menopausal hair loss:
- Hormonal Changes: When women go through menopause, the levels of estrogen and progesterone hormones in their bodies decrease. These hormones are important for hair growth. When they decrease, it can affect the normal hair growth cycle and make hair thinner and fall out more easily.
- Testosterone Influence: Women also have a little testosterone, a hormone usually associated with men. When estrogen levels decrease during menopause, the balance between estrogen and testosterone changes. This shift can affect hair follicles and cause hair loss.
- Aging: As we age, our hair follicles weaken and produce thinner hair. This natural aging process can make hair look less full and make it easier to fall out.
- Genetic Predisposition: Sometimes, hair loss during menopause can run in families. If your close relatives experienced hair thinning or loss during menopause, you might also be more likely to experience it.
- Other Factors: Certain health conditions like thyroid problems or PCOS can contribute to hair loss during menopause. Factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and certain medications can also make hair loss worse.
The Cycles of Hair Growth
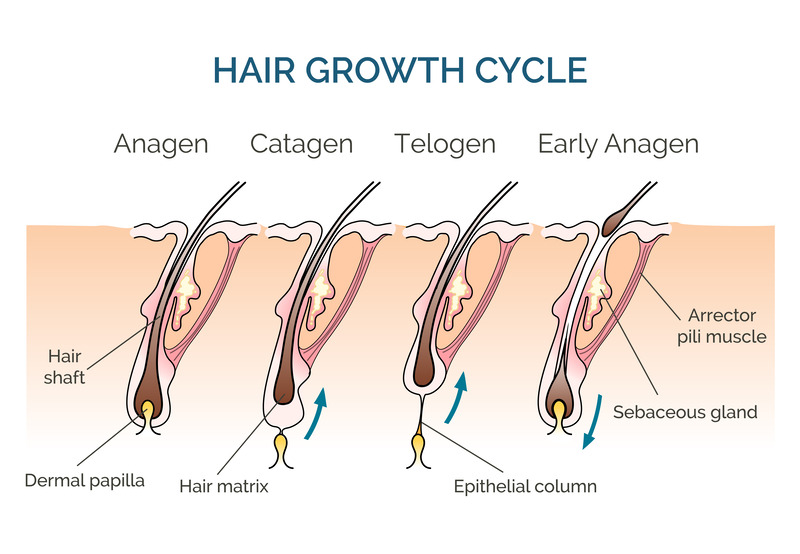
Hair growth occurs in cycles; understanding these cycles can help us better grasp the process. Here are the main stages of hair growth:
- Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): This is the active phase of hair growth. The hair follicles actively produce new cells, and the hair strand grows longer. The duration of this phase varies for each individual, typically lasting between 2 to 7 years. The length of hair during this phase is determined by genetics and overall health.
- Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): In this short transitional phase, the hair follicle stops producing new cells. It separates from the blood supply, and the hair strand no longer grows. This phase lasts for about 1 to 2 weeks.
- Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): The hair follicle remains inactive during this phase. The hair strand is fully formed but not growing. It stays attached to the scalp while new hair forms underneath it. This phase lasts for approximately 3 to 4 months.
- Exogen Phase (Shedding Phase): This is the final phase of the hair growth cycle. The old hair strand sheds and the new hair strand emerges from the follicle to start a new growth cycle. It’s normal to shed about 50 to 100 hairs daily during this phase.
How to Treat Menopausal Hair Loss
When it comes to treating menopausal hair loss, various options are available to help manage and improve the condition of your hair. Let’s explore these treatments in more detail:
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone replacement therapy involves using medications that contain hormones, such as estrogen, to balance hormone levels in your body. This can help reduce hair loss and encourage hair growth.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional to understand HRT’s potential risks and benefits.
Medications
Certain medications, like minoxidil, can be applied topically to your scalp. Minoxidil is available over the counter and works by stimulating hair follicles, promoting hair growth, and preventing further loss.
You can easily incorporate it into your daily hair care routine.
Scalp Massage
Massaging your scalp with your fingertips in gentle, circular motions can increase blood circulation to your hair follicles. This improves nutrient delivery to the hair roots, creating a healthier environment for hair growth.
Plus, it feels relaxing and can be a soothing self-care practice.
Nutritional Supplements
Specific supplements, such as biotin, B-complex vitamins, zinc, and iron, can help support hair health. These nutrients play a vital role in maintaining strong and healthy hair.
Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right supplements and dosages.
Laser Treatment and Microneedling
These are non-invasive procedures performed by professionals in specialized clinics. Laser treatment uses low-level laser therapy (LLLT) to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
Microneedling involves creating tiny punctures in the scalp to encourage collagen production and enhance the absorption of topical treatments. Both procedures can help improve hair density and overall hair health.
Hair Transplant
The hair transplant surgery may be an option in more severe hair loss cases. This procedure involves moving hair follicles from areas of the scalp with good hair growth to thinning or balding areas.
It’s a more invasive treatment and should be discussed thoroughly with a healthcare professional or hair transplant specialist.
Eating a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for overall health, including the health of your hair. Ensure to consume various nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
These provide the vitamins, minerals, and proteins necessary for healthy hair growth and maintenance.
Gentle Hair Care Practices
Handling hair with care is important to minimize damage and hair breakage. Use mild shampoos and conditioners specifically formulated for your hair type.
Avoid excessive heat stylings tools like straighteners, curling irons, and tight hairstyles that can strain and weaken your hair. Harsh chemical treatments should also be avoided, as they can cause further damage.
Camouflage Techniques
If you’re concerned about the appearance of thinning hair, there are styling techniques you can try to make your hair look fuller. For example, layering your hair or using volumizing products can create the illusion of thicker hair.
Additionally, hairpieces can provide temporary coverage for thinning areas, giving you more confidence.
Remember, results can vary for each person, and being patient and consistent with your chosen treatment is important. Consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the most suitable approach for your situation.
They can evaluate your hair loss pattern, medical history, and lifestyle factors to provide personalized advice and guidance. Together, you can find the best treatment plan to manage and improve your menopausal hair loss.
How to Prevent Menopausal Hair Loss?

While you can’t completely stop menopausal hair loss, there are things you can do to reduce its impact and keep your hair healthy. Here are some simple tips:
1. Eat a Healthy Diet: A well-rounded diet that includes essential vitamins and minerals is important to promote healthy and restore hair growth. Here are some key nutrients to focus on:
- Vitamin B12: Found in animal products like meat, fish, and dairy, vitamin B12 supports the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen and nutrients to the scalp and hair follicles.
- Iron is crucial for proper hair growth as it helps deliver oxygen to the hair roots. Good sources of iron include lean meats, beans, spinach, and fortified cereals.
- Niacin (Vitamin B3) and Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5): These vitamins improve blood circulation to the scalp, promoting a healthy environment for hair growth. Niacin can be obtained from foods like poultry, fish, peanuts, and mushrooms, while pantothenic acid is found in avocados, broccoli, and whole grains.
- Vitamin A is essential for sebum production, moisturizing the scalp, and keeping hair healthy. Include foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens in your diet for a natural source of vitamin A.
- Zinc: Zinc plays a role in DNA and protein synthesis, which are necessary for healthy hair growth. Foods like oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, and lentils are good sources of zinc.
2. Biotin (Vitamin B7): Biotin promotes hair strength and thickness. It can be found in eggs, nuts, seeds, and sweet potatoes.
3. Be Gentle with Your Hair: Treat your hair gently to avoid damage. Use mild shampoos and conditioners that are good for your hair type. Avoid using too much heat on your hair, harsh chemicals, and tight hairstyles that can harm your hair.
4. Massage Your Scalp: Sometimes, massaging your scalp with your fingertips can help. It increases blood flow to your scalp and can promote healthy hair growth.
5. Manage Stress: Find healthy ways to manage stress because it can contribute to hair loss. Do things that help you relax, like exercising, meditating, or enjoying hobbies.
6. Quit Smoking: Consider quitting or cutting back if you smoke. Smoking can harm your hair and make it more likely to fall out.
7. Stay Hydrated: Drink enough water to hydrate your body and hair. This is important for healthy hair growth.
8. Exercise Regularly: Try to stay active and exercise regularly. It promotes overall health and good blood flow, benefiting your scalp and hair.
9. Talk to a Doctor: If you’re worried about your hair loss, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor. They can look into your situation and give you advice or recommend treatments or supplements that might help.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If you are experiencing menopausal hair loss and have concerns, it is recommended to see a healthcare provider. They can assess the severity of your hair loss, identify any underlying causes, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options.
It is especially important to seek medical advice if you are experiencing excessive or rapid hair loss in women, have other accompanying symptoms, or have a family history of significant hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional will help you receive proper evaluation and personalized care.
Final Thoughts
Experiencing hair loss during menopause can be challenging and stressful for many women. However, it’s important to understand that it is a natural part of the hormonal changes that occur during this stage of life. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide you with the proper diagnosis, guidance, and treatment options to address your needs.
In addition to seeking professional advice, exploring products and supplements that promote hair health can be beneficial. For example, vitamins Revive offers a range of hair products and supplements specifically formulated to support and nourish your hair from within. Their high-quality formulations can help enhance your hair health and promote stronger, more vibrant hair.
Take the first step towards managing menopausal hair loss and visit the Vitamins Revive collection to explore their range of hair products and supplements. By investing in your hair health, you can regain confidence and enjoy healthier-looking hair. Remember, with the right support and proactive measures, and you can navigate through menopausal hair loss with ease and embrace your natural beauty.
FAQs
Will hair loss from menopause grow back?
Yes! It is possible for hair loss from menopause to grow back. While most forms of hair loss are permanent, hormonal hair loss may be reversible after the period of menopause ends.
What is female pattern hair loss?
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is a type of hair loss that can affect menopausal women. It is often characterized by gradually thinning hair on the scalp, which usually occurs at the top and along the sides of the head.
What are the symptoms of menopausal hair loss?
Menopausal hair loss symptoms primarily involve thinning hair and receding hairlines. Additional signs may include increased shedding, dryness in the scalp, and dullness in the hair. Other menopausal symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, weight gain, irregular periods, and mood swings/depression.









